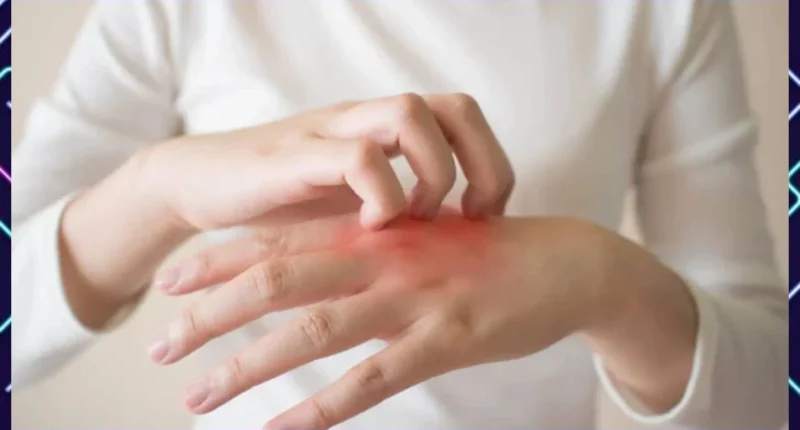
Many people worry that a psoriasis diagnosis means a life sentence of itchy, red patches. While there currently isn’t a permanent cure, early intervention and finding the right treatment plan for psoriasis can make a big difference. In fact, with proper care, this condition can be effectively managed.
The truth is, millions around the world – about 3% of the population – live with psoriasis, JAMA Dermatology. Despite how common it is, a lack of awareness and stigma can prevent people from seeking help. Psoriasis isn’t contagious, but it can be socially embarrassing, especially when the condition flares up on visible areas like the scalp, elbows, or knees.
This chronic skin condition causes the body to overproduce skin cells, leading to those telltale patches. Psoriasis can take many forms, appearing as small, barely noticeable spots or large, inflamed areas. The good news? Treatment options vary depending on the type and severity of your psoriasis. A dermatologist can work with you to create a personalized plan to manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life.
Also read: 7-Day Psoriasis Diet Plan: Nourish Your Skin from Within
While psoriasis primarily affects the skin, leaving it untreated can have consequences reaching far beyond. Here’s a look at some potential health complications:
- Inflammation and pain in joints. This is called psoriasis arthritis. It can make it difficult for a person to work and walk.
- Inflammatory diseases
- Heart conditions
- Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Lupus
- Obesity
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Suicidal tendencies and depression
- Trauma and shame
- Pneumonia
- Septicemia
- Heart failure
- Conjunctivitis and other eye conditions
- Pregnancy complications
- PCOS
Psoriasis can be much more than just physically uncomfortable (itching, redness, etc.). It can also have a lasting emotional impact (anxiety, depression) on people with the condition. This can affect anyone, but it’s most common in men, women, and children between 15 and 35 years old. Here’s why early diagnosis is crucial:
- Many people might not know they have this condition, mistaking it for dry skin or another condition.
- Psoriasis can sometimes be misunderstood, leading to social isolation or feelings of being judged.
- An accurate diagnosis from a dermatologist (a skin doctor) is key to getting the right treatment and managing the condition effectively.
The good news? Psoriasis is often treatable, especially when caught early. So, if you’re experiencing any skin problems, don’t hesitate to visit a dermatologist for a checkup. It could be the first step to feeling better, both physically and emotionally.
Cause of Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic, inflammatory skin condition that has been documented in medical records dating back to the 1800s. However, the origins of this itchy and scaly condition can be traced even further, with its name derived from the Greek word “psora,” meaning “itch.”
The primary healthcare professional responsible for treating psoriasis is a dermatologist, as the condition primarily manifests on the skin. However, it is important to note that psoriasis is not solely a dermatological issue, but rather an autoimmune disorder.
In psoriasis, the body’s white blood cells become overactive, leading to the excessive production of cytokines. This autoimmune malfunction triggers a cascade of chemical reactions in the skin and other organs, ultimately causing an accelerated multiplication of the cells in the outer layer of the skin, known as keratinocytes. While the normal rate of skin cell multiplication is around one month, in individuals with psoriasis, this rate can be as rapid as three to five days.
The most common symptom of psoriasis is the accumulation of dead skin cells, resulting in the formation of patches and silvery, scaled areas on the skin. These visible manifestations are just the tip of the iceberg, as the effects of psoriasis can extend beyond the skin, impacting the overall health and well-being of the individual.
Ongoing worldwide research continues to explore the underlying causes of psoriasis, with genetics and environmental factors emerging as the two primary suspects. Understanding the complex nature of this autoimmune disorder is crucial for healthcare professionals and patients alike, as it paves the way for more effective management and treatment strategies.
Early Treatment of Psoriasis
Psoriasis, an autoimmune disorder, often faces a significant barrier to early treatment due to the stigma and lack of awareness surrounding the condition. However, with proper understanding and a proactive approach, individuals with psoriasis can manage their symptoms effectively and lead a fulfilling life. Research found various aspects of psoriasis treatment, including identifying triggers, topical treatments, phototherapy, systemic treatments, and the latest advancements in biologics.
Identifying and Avoiding Triggers
Psoriasis can be triggered by various factors, including infections, weather changes, injuries, stress, smoking, alcohol consumption, certain medications, and sudden withdrawal from some systemic drugs. By recognizing and avoiding these triggers, individuals with psoriasis can better manage their symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
Topical Treatments
Moisturizers are an essential part of psoriasis management, as they help to hydrate and soothe the skin. It is crucial to choose fragrance-free moisturizers to minimize irritation. Other topical treatments for psoriasis include steroids, coal tar creams, and vitamin A and D creams. These treatments work by reducing inflammation, slowing skin cell growth, and improving the appearance of lesions.
Phototherapy
Phototherapy is a treatment option that involves exposing the affected areas of the skin to controlled amounts of ultraviolet (UV) light. This can be achieved through the use of lasers, sunlight, UVA, or UVB treatments. Phototherapy helps to slow down the growth of skin cells and reduce inflammation, leading to clearer skin.
Systemic Treatments
In cases where topical treatments and phototherapy are not effective, systemic treatments may be prescribed. These treatments work by targeting the underlying causes of psoriasis throughout the body. Retinoids and methotrexate are examples of systemic treatments used in the management this condition.
Biologics
Biologics are a newer class of medications that target specific parts of the immune system to reduce inflammation and slow the progression of psoriasis. These treatments are particularly effective in managing severe cases of the condition. Biologics have revolutionized the treatment of this condition, offering hope to those who have not responded well to traditional therapies.
It is essential to remember that early treatment is crucial in managing this condition. Delaying treatment or relying too heavily on home remedies can lead to worsening symptoms and an increased risk of complications. Regular communication with a dermatologist is key to developing an effective treatment plan and monitoring progress.
Patients should also be aware that the symptoms they experience today may not be indicative of future flare-ups. Joining support groups and connecting with others who have similar experiences can help individuals with psoriasis better understand their condition and feel less alone.
In conclusion, overcoming the stigma and raising awareness about this condition is crucial for promoting early treatment and improving the quality of life for those affected by the condition. By working closely with dermatologists, identifying and avoiding triggers, and exploring the various treatment options available, individuals with psoriasis can manage their symptoms effectively and lead a happy, healthy life.