What are the “5 Things to Know About Mycoplasma Pneumoniae”? Mycoplasma pneumoniae is a bacterium that can cause respiratory illness, including pneumonia. Here are five key facts about Mycoplasma pneumoniae:
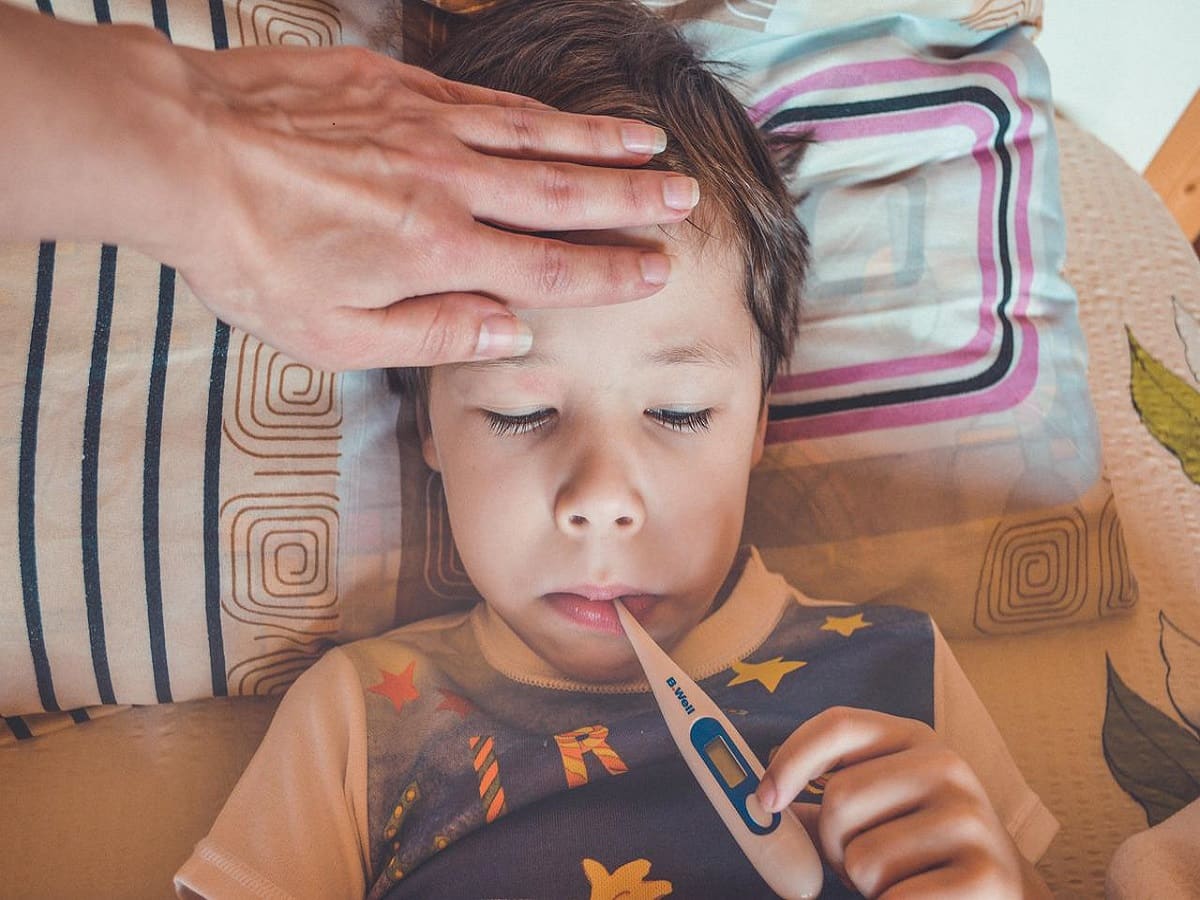
- Symptoms: Typical symptoms of Mycoplasma infection include fever, cough, bronchitis, sore throat, headache, and tiredness. It can also cause “walking pneumonia,” which is usually mild and rarely requires hospitalization. Infections of the middle ear (otitis media) can also result.
- Who is Affected: Anyone can get the disease, but it most often affects older children and young adults. Mycoplasma infections occur sporadically throughout the year, with widespread community outbreaks also possible. The infection is most common in late summer and fall.
- Diagnosis and Spread: Mycoplasma infection is usually diagnosed based on typical symptoms and a chest x-ray. Blood tests may be done. The bacterium is spread through contact with droplets from the nose and throat of infected individuals. Good hand hygiene and cough etiquette are important for preventing infection.
- Atypical Nature: Pneumonia caused by M. pneumoniae is considered “atypical” because the symptoms and duration of sickness are different than typical pneumonia. The infection can appear differently on a lung x-ray. M. pneumoniae can cause different types of respiratory infections other than pneumonia, such as tracheobronchitis or a chest cold.
- Treatment and Prevention: Mycoplasma pneumonia usually affects people younger than 40. Most cases of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection are mild and can be treated with antibiotics. However, there are no vaccines for the prevention of Mycoplasma infection, and good hand hygiene and cough etiquette are important for preventing its spread.
Source: [1]
How Is mycoplasma pneumoniae transmitted
Mycoplasma pneumoniae is transmitted from person to person through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. The bacteria can also be spread through prolonged close contact with an infected person, especially in crowded settings like schools, college residence halls, military training facilities, long-term care facilities, and hospitals. The contagious period is probably fewer than 10 days and occasionally longer. Mycoplasma infections occur sporadically throughout the year, with widespread community outbreaks also possible. Anyone can get the disease, but it most often affects older children and young adults. Good hand hygiene and cough etiquette are important for preventing its spread.
How long does It take for symptoms of mycoplasma pneumoniae infection to appear
Symptoms of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection usually appear after 1 to 4 weeks of exposure to the bacteria. However, symptoms can last for several weeks. Children younger than 5 years old who get Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection could have symptoms that are similar to a cold, such as sneezing, stuffy or runny nose, sore throat, watery eyes, wheezing, vomiting, and diarrhea. Pneumonia (lung infection) can also occur, and common symptoms of pneumonia include fever, chills, cough, feeling tired, and shortness of breath. The contagious period is probably fewer than 10 days and occasionally longer. Good hand hygiene and cough etiquette are important for preventing its spread.
ALSO READ: 5 Conditions That Cause Swelling In The Legs And Feet
What are the complications of mycoplasma pneumoniae infection?
Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection can lead to several complications, especially in children and the elderly. Some of the complications include:
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
- Bronchiolitis obliterans
- Lobar consolidation
- Lung abscess
- Necrotizing pneumonitis
- Pleural effusion (15% to 20%), empyema (rare)
- Respiratory failure
Extrapulmonary complications can also occur, such as immune thrombocytopenic purpura, acute hepatitis, autoimmune hemolytic anemia, arthritis, and transverse myelitis. Severe complications are uncommon but can result in hospitalization and sometimes death. Other complications involving the respiratory system include exacerbation of asthma and severe pneumonia. Additionally, Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections can cause or worsen complications such as encephalitis, hemolytic anemia, renal dysfunction, and various skin disorders like Stevens-Johnson syndrome, erythema multiforme, and toxic epidermal necrolysis [Sources: 2, 3, ]
Long-term Effects
Long-term effects of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection can vary, but some studies have reported chronic respiratory infection, airway hyperreactivity, and pulmonary inflammation in murine models. In humans, M. pneumoniae has been reported to be detectable by culture of the respiratory tract for up to six weeks after treatment with effective antibiotics. While the long-term effects of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection are not well-documented, complications involving the respiratory system can occur, such as exacerbation of asthma and severe pneumonia. Additionally, Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections can lead to immune dysregulation, which can result in cerebellar dysfunction, late-onset transverse myelitis, and peripheral nerve involvement [Sources: 4, 5].
DON’T MISS: Athlete’s Foot Condition: Symptoms, Causes and Treatment