Deep Brain Surgery: Which Patients Are Eligible For DBS? Get to find out in this article.
Deep Brain Surgery: Which Patients Are Eligible For DBS? Get to find out in this article.
Deep brain surgery is a surgical procedure in which electrodes are implanted in certain areas of the brain. These electrodes produce electrical impulses which block or regulate abnormal brain activity.
Which Conditions Can Be Treated Using DBS?
Deep brain stimulation is useful for patients with movement disorders that cannot be controlled using medications, these include:
- Essential tremor
- Parkinson’s disease
- Epilepsy
- Psychiatric disorders like obsessive-compulsive disorder
- Dystonia (a movement disorder in which there are involuntary muscles contractions leading to repetitive or twisting movements)
There are ongoing trials to study the use of DBS for conditions such as Tourette’s syndrome, chronic pain, and Huntington’s disease.
Components Of DBS system
The DBS system has three essential components:
- Electrodes: These are thin insulated wires which are inserted through a small opening in the skull and placed on the target area of the brain.
- Implantable pulse generator: It is like a pacemaker device that generates the impulses. It is placed under the skin in the chest region.
- Extension leads: These are thin insulated wires which carry the impulses from the pulse generator to the electrodes.
Deep Brain Surgery: Which Patients Are Eligible For DBS?
DBS is a complex procedure, a lot of assessments, tests, and procedures need to be done before and after the surgery. Moreover, the procedure is expensive. Thus, the first criterion is that the patient should be ready to commit to the procedure.
Parkinson’s disease
The following patients with Parkinson’s disease can benefit from DBS:
- Patients who have severe, uncontrolled tremors cannot be managed with medications.
- For patients who respond well to medications but have severe motor symptoms like dyskinesia, once the effect of the medication wears off
- Patients who do respond to high doses of medication but are unable to tolerate its side effects.
Dystonia
DBS can help patients with dystonia who are refractory to medications. However, the response of a patient to DBS depends on the cause of dystonia.
DBS may not be recommended in the following cases:
- When the chief issue in the patient is difficulty in maintaining balance, difficulty in walking, or ‘freezing’ episodes.
- When the primary symptom of the patient is speech difficulty
- When a patient is confused and has problems with memory and thinking
- When a patient has conditions like depression or anxiety which has not been controlled with other treatment
- When a patient has a health issue in which surgery is contraindicated.
Procedure for DBS
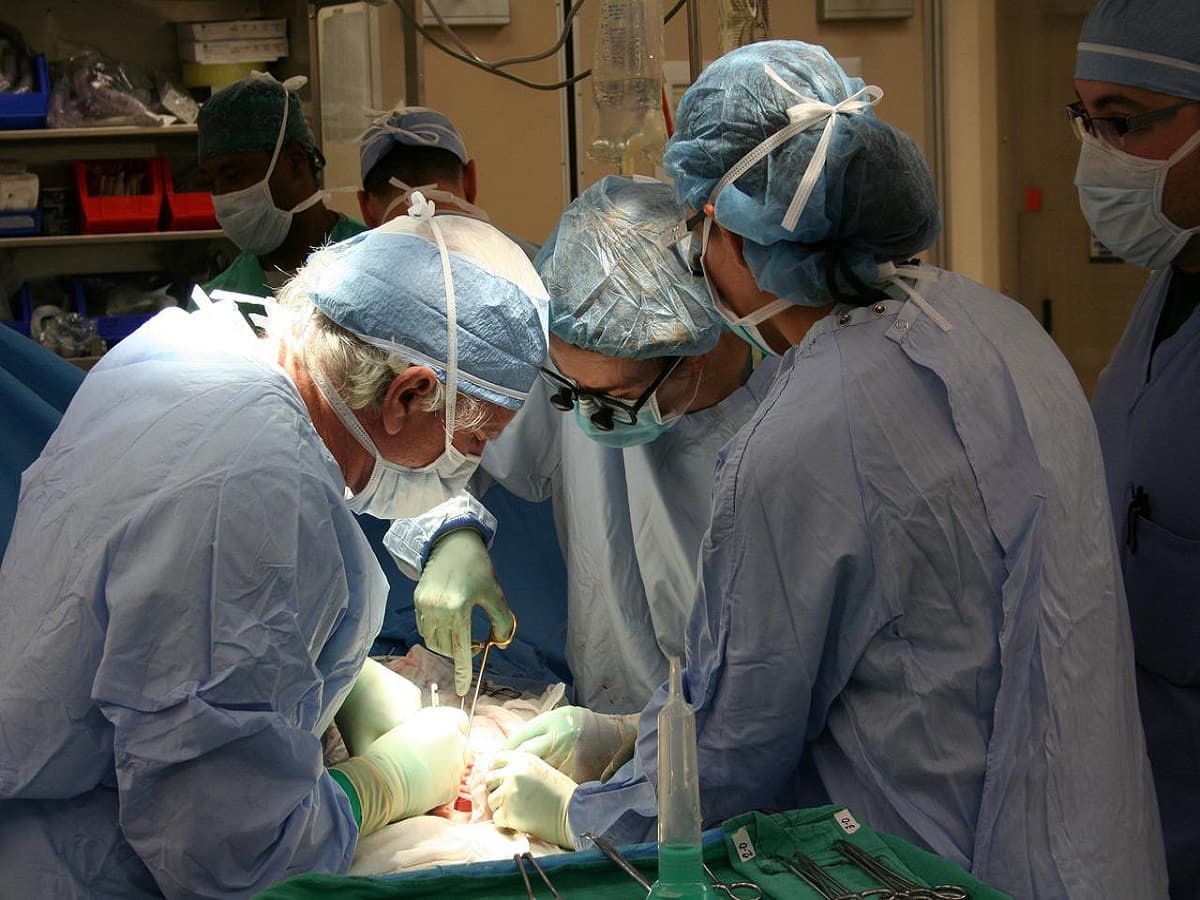
The procedure of DBS involves two surgeries: Brain surgery for implanting the electrodes and chest wall surgery to implant the pulse generator.
Brain surgery
First, a special head frame is placed on the patient’s head to keep the head still during the procedure. Then, the care team would perform neuroimaging (CT or MRI) to identify and assess the area where the electrodes need to be implanted. The patient is usually awake during the surgery. A local anaesthetic is administered to numb the scalp before the surgery. Anaesthesia is usually not needed because the brain does not have pain receptors.
The surgeon implants a thin wire with electrodes at the end of the target area. The wire runs under the skin and is connected to the pulse generator present in the chest region.
Chest surgery
The pulse generator is implanted under the skin below the collarbone. This procedure requires general anaesthesia. The pulse generator continuously sends impulses to the brain, but it can be controlled (on/off) using external remote control.
After a few weeks of surgery, the doctor would activate the pulse generator using a remote control. The amount of stimulation depends on the type and severity of the patient’s condition. The doctor may recommend constant stimulation or may ask you to switch off the stimulator at night using the remote control.
Preparation before the procedure
Prior to surgery, the patient needs to undergo various tests to check if the patient needs DBS and is an eligible candidate for DBS:
- Blood/ urine tests: To assess the general health of the patient and if the patient is fit for surgery.
- Special tests:Electroencephalography for epilepsy, neuropsychological evaluations, etc.
- Cognitive assessment: To check/determine whether the patient will be able to participate in the procedure
If the patient has Parkinson’s, the doctor should check the patient’s symptoms and whether he/she is responsive to medications.
Care After Procedure
The patient would have to stay in the hospital for 1-2 days after the procedure. The stitches are removed around 14 days after surgery. The patient needs to follow these care instructions:
- The pin sites should be covered with a band-aid and should be changed daily as necessary
- The Head can be sponged using a damp cloth; the surgical area must be avoided.
- Hair can be gently shampooed only after the stitches are removed
- The surgical area must not be scratched.
- The patient should not take part in light activities like household chores for 2 weeks after surgery. Heavy intense activities should be avoided for 4-6 weeks after surgery.
- Heavyweights should not be lifted for at least 2 weeks post-surgery.
Advantages Of DBS
Deep brain stimulation has many advantages:
- DBS is a reversible technique.
- DBS doesn’t permanently damage any part of the brain.
- Stimulation can be adjusted according to the changes in disease and response to medications.
- DBS can be turned off using an external remote control if the patient experiences excessive side effects.
Risks And Complications Of DBS
Like any medical procedure, DBS also has certain risks and may lead to potential complications
- Complications related to surgery: Brain infection or haemorrhage, misplacement of the electrodes
- Complications related to the hardware: Lead failure, battery failure
- Complications related to stimulation: The patient may experience symptoms like freezing, involuntary movements, speech issues, balance and gait issues, and tingling/ numbness during stimulation. These side effects are temporary and go away when the device is adjusted.
Prognosis
In carefully selected patients, DBS has been found to be a very safe and effective treatment to control symptoms. The symptoms do not completely go away but the severity is reduced to a great extent.