What are the Common Fungal Infections In Summer? A look at the concept.
 Fungal infections increases during the summer due to hot and humid weather conditions and excessive sweating. Below are expert tips to keep fungal infections at bay.
Fungal infections increases during the summer due to hot and humid weather conditions and excessive sweating. Below are expert tips to keep fungal infections at bay.
Summer does not just aggravate gastrointestinal problems, but also fungal infections. The rise in temperature along with humid conditions has led to a surge in the number of patients with fungal infections. As the temperature is set to further increase in the coming days, doctors have warned that fungal infections will also start to shoot up.
Fungal infections increase during the summer as a hot environment encourages fungi growth. Lack of personal hygiene further adds to the woes, increasing the number of fungal infections every year.
Hence, they are advising people to take utmost care, follow good personal hygiene, wear loose cotton clothes, and seek prompt treatment if they develop fungal infections.
Common fungal infections in summer and their causes
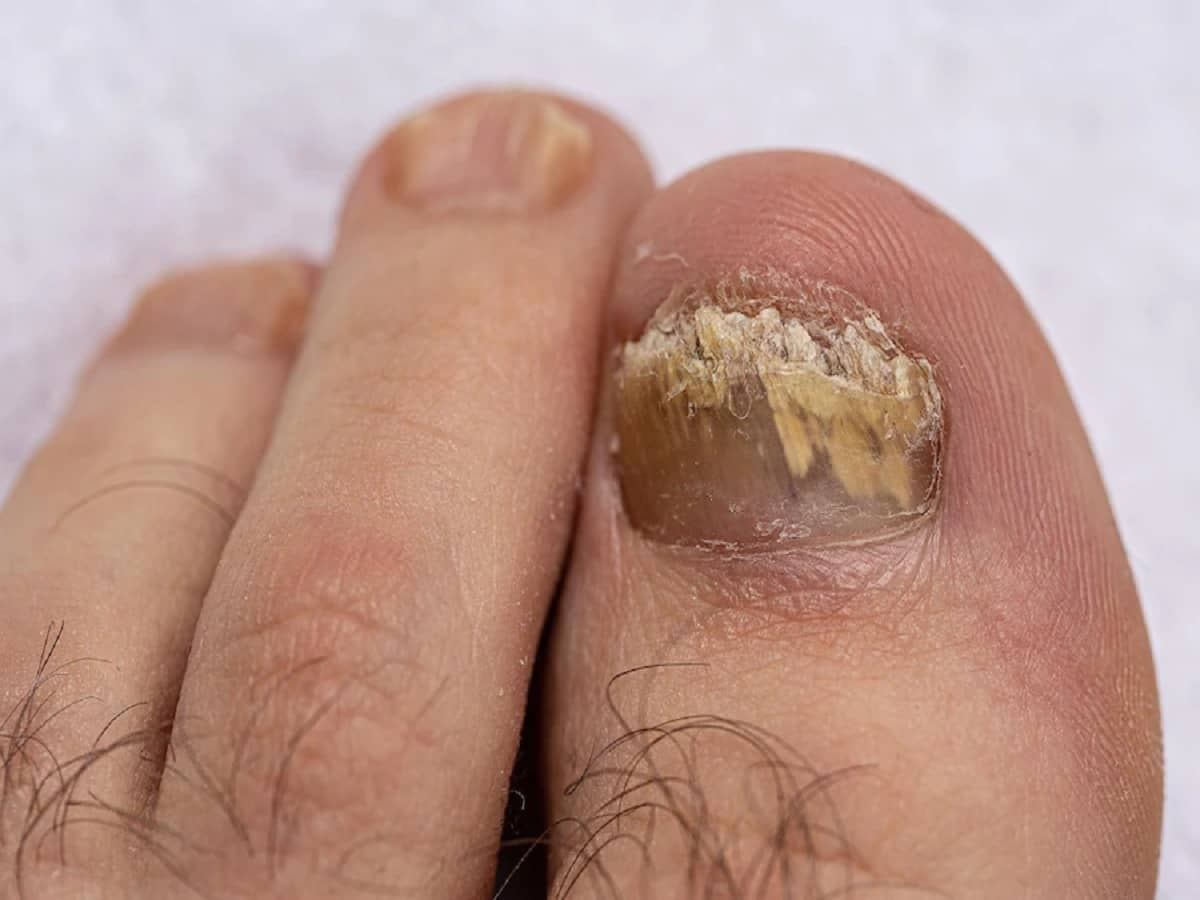
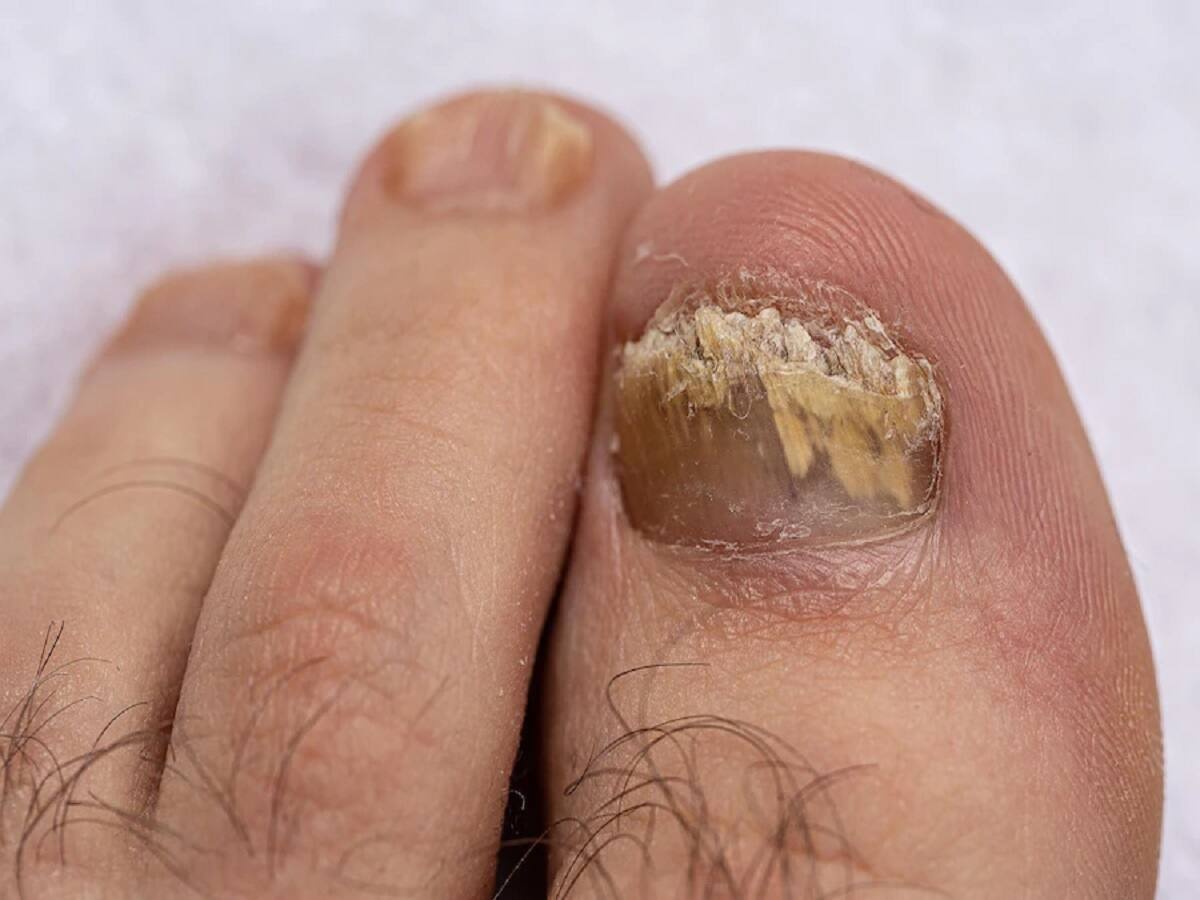
Fungal skin infections can be seen anywhere on your body. Fungal infections such as ringworm, athlete’s foot, toenail fungus, yeast infections, and rashes in the genital area are a growing matter of concern, according to the doctors.
Dermatophyte infections are common occurrences. These contagious fungal infections occur on the feet (tinea pedis, or athlete’s foot), or anywhere else on the body where sweat can easily accumulate, like the under your armpits or breasts (tinea corporis). Dermatophyte infections are also seen on fingernails and toenails. These infections lead to excessive itching, redness, and swelling in the affected areas.
Another commonly seen fungal infection is Tinea versicolor that causes lighter or darker patches of skin. It’s caused by a fungus on the skin that grows out of control, said Dr Pradeep Alate, Paediatrician, Apollo Spectra, Pune.
Vaginal yeast infection happens due to the fungus Candida albicans that causes inflammation and irritation around the vagina. Steroid overuse was the main reason for the increase in the number of mucormycotic patients in the corona period, added Dr. Alate.
Moreover, doctors are seeing more cases of skin dryness and prickly heat rashes.
Treatment of fungal infections
Dr Tushar Parikh, Chief Neonatologist and Paediatrician, Motherhood Hospital, Pune, recommended using medication, creams or lotions suggested by the doctor for treatment of fungal infections. However, he cautioned people against use of steroid-containing creams.
“Complete the treatment course given by the doctor, wash clothes and undergarments daily, maintain good personal hygiene, and use antifungal soap and powder after consulting the doctor. Wash hands to prevent spreading the infection from one area of the body to another. Don’t share towels or clothing as they can spread the fungus. Avoid athlete’s foot by changing the socks every day,” said Dr. Parikh.
To keep fungal infections at bay, Dr. Parikh suggested:
- Avoid wearing tight clothes, jeans and shoes, and keep nails short
- Don’t wear sweaty clothes for a longer time
- Keep yourself dry, wear loose cotton clothes
- Try to stay clean and dry during summer
- Do not use scented or chemical products on the infected area as they can cause irritation and rashes.
- Avoiding processed foods as high sugar levels trigger infections and slow down the healing process.
- Include garlic in the diet by adding it to the soup or curry as it is anti-fungal in nature.
- Keeping the skin dry is important, particularly in areas like groin, armpits and neck.
How to protect kids fromfungal infections
Parents are being advised to ensure that their child wears loose cotton clothes and remains in relatively cooler rooms in the house. Parents should not allow children to step out of house during the afternoon, and encourage using sunscreen for kids, which should be applied 20 min before stepping out of the house. Sensitive skin can develop skin burns if sunscreen is not applied or proper precautions not taken, the doctors stated.
There is also an increase in the cases of dehydration, heat stroke, gastroenteritis, and loose motions among kids, noted Dr Parikh
“Ensure your child remains well hydrated with frequent offering of water to him or her. Also give juicy fruits like watermelon. Ensure the child is passing adequate urine which indicates good hydration status of the child. Ensure you give clean water to child to drink. Avoid water from open taps or unhygienic sources,” said Dr Parikh.