If you experience stomach problems frequently, there are several steps you can take to revitalize your gut and enjoy optimal health.
The general health of your digestive system, especially the composition of your gut microbiome, is referred to as gut health. Your large intestine is home to a vast community of trillions of bacteria, viruses, and fungi, collectively known as your microbiome. These microorganisms, act accordingly in breaking down nutrients to make them accessible to your body. These tiny residents of your gut are more than just passengers; they perform some vital tasks:
- helps break down food components that your body wouldn’t be able to digest on its own, allowing you to absorb essential nutrients
- helps train your immune system to differentiate between harmless substances and potential pathogens.
- Producing hormones that help regulate appetite, satiety, and metabolism.
- Communicating with the brain through the vagus nerve to influence mood, cognitive function, and overall well-being.

According to a study published in Nature, gut bacteria serve several functions, such as fermentation of food, protection against pathogens, stimulating immune response among many
When your gut health is compromised, it can have significant negative impacts on your overall well-being. Harmful bacteria can dominate the gut microbiome, leading to various health issues. One study by the International Journal of Molecular Science found that diseases such as inflammatory bowel diseases, obesity, diabetes, liver diseases, chronic heart diseases, cancers, HIV, and autism are related to gut bacteria
ALSO READ: 11 Low Fiber Vegetables for Constipation – Natural Remedies for Digestive Health
To restore balance and promote healthy living, here is a detailed explanation of how best you can Revitalize your Gut:
Revitalize Your Gut: Eleven Simple Steps to Boost Digestive Health
To enhance your gut health through lifestyle and dietary modifications, consider the following strategies:

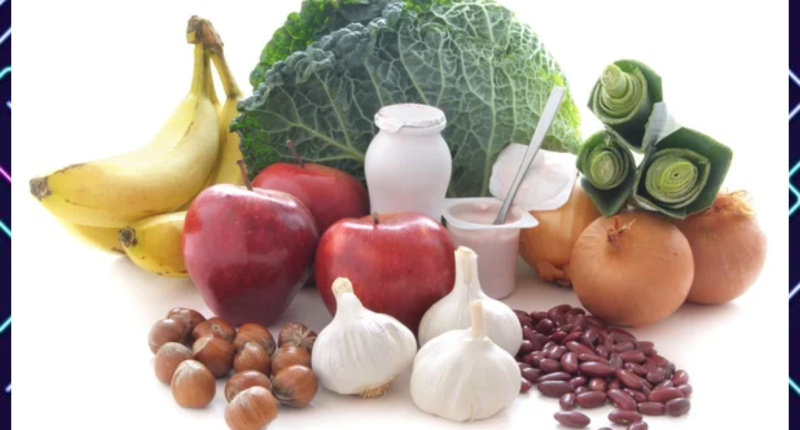
1. Incorporate More Fiber-Rich Foods: Fiber plays a pivotal role in digestive health, influencing gut functions, aiding digestion, and facilitating nutrient absorption. Studies, such as those published in the National Library of Medicine, highlight how gut bacteria metabolize fiber to safeguard against gastrointestinal disorders. Opt for fiber-rich foods like vegetables, beans, legumes, fruits, nuts, seeds, berries, oatmeal, brown rice, bran cereal, and whole-wheat pasta to bolster your digestive system.
2. Diversify Your Diet: Embrace a wide array of fruits, vegetables, and nutrient-dense foods to enrich your diet with a broad spectrum of vitamins, minerals, and other essential nutrients. Diversifying your diet fosters a more varied gut microbiome, contributing to overall gut health. Increasing plant-based foods, as suggested by research in the Nutrients journal, enhances the presence of beneficial gut bacteria.
3. Minimize Ultra-Processed Foods: While some degree of processing is inevitable, opting for less processed foods is advisable. Research in Nature Reviews Gastroenterology and Hepatology indicates that ultra-processed foods (UPFs) and additives can elevate the risk of gut-related diseases, including inflammatory bowel disease, irritable bowel syndrome, and colorectal cancer. Focus on obtaining nutrients from plant-based foods and lean proteins instead.
4. Maintain Proper Hydration: Water serves as a natural lubricant, easing the passage of food through the digestive tract. A study in the Journal of Nutrition revealed that increased water consumption correlates with reduced bacteria linked to gastrointestinal issues. Aim for 8-10 glasses of water daily to prevent complications and promote gut health.
5. Ensure Adequate Sleep: Beyond its direct benefits, sleep influences gut health indirectly. Insufficient or poor-quality sleep can compromise gut health, as evidenced by studies like those published in PLOS ONE. Strive for uninterrupted sleep of 7-8 hours nightly to mitigate potential gut issues.
6. Practice Mindful Eating: Eating slowly and chewing food thoroughly not only aids digestion but also contributes to better gut health. A Nature Research study found that slow eating, which involves chewing food slowly and thoroughly, is an effective strategy for controlling appetite and digestion. This approach reduces risks associated with obesity and diabetes, encouraging mindful food choices.
7. Consider Probiotics: Probiotics, comprising “good” bacteria and yeasts, are integral to digestive health. They help regulate the gut microbiome and fortify the intestinal barrier, potentially preventing digestive disturbances. Probiotic-rich foods include yogurt, cheese, kimchi, kombucha, kefir, tempeh, and sauerkraut, as supported by research in Microb Biotechnology.
8. Acknowledge and Address Food Intolerances: Consuming foods that your gut struggles to process can exacerbate digestive discomforts. Recognizing signs of food intolerance is crucial for anyone seeking to optimize their gut health. If you notice symptoms such as nausea, fatigue, acid reflux, gas, diarrhea, abdominal pain, or bloating after eating certain foods, it’s advisable to eliminate those items from your diet.
9. Enhance Your Diet with Collagen-Rich Foods: Collagen, a vital protein synthesized by your body, is instrumental in providing structural support and strengthening components like bones, muscles, skin, and connective tissues. Additionally, it holds significance for gut health. Research highlighted in Polymers underscores collagen’s positive impact on the gut microbiome, though further studies are needed to fully understand its benefits. Incorporating collagen-rich foods such as broccoli, citrus fruits, eggs, nuts, and meat into your diet can contribute to overall gut well-being.
10. Incorporate Garlic for Gut Health: Garlic stands out as a valuable component of a diet aimed at enhancing gut health. It offers numerous benefits, including supporting intestinal health and reducing inflammation. Moreover, garlic may aid in eliminating intestinal parasites and safeguarding gut health. A study featured in the Nutrients journal demonstrated that garlic consumption could enhance gut health and diversify the gut microbiome in animal models.
11. Manage Stress Levels: Chronic stress can have a profound impact on your overall health, including your gut. Research published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences suggests that prolonged stressors can negatively affect both brain and gut health. To avoid complications, it is crucial to maintain healthy stress levels. This can be achieved through stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga. By keeping stress levels in check, you can help mitigate the negative effects on your gut health.
ALSO READ: Who should avoid eating cruciferous vegetables? These group of people
Common Signs of Unhealthy Gut

Digestive issues: This can include frequent gas, bloating, constipation, diarrhea, heartburn, and abdominal pain. These symptoms can all be signs that your gut is having a hard time processing food and eliminating waste.
Fatigue: People with chronic fatigue may have imbalances in the gut. A study found that almost half of people with fatigue also had IBS.
Skin problems: Skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis may be related to the types of bacteria present in the gut.
Food intolerances: Food intolerances may be caused by poor quality of bacteria in the gut. You may have a food intolerance if you struggle to digest certain foods, like dairy or gluten. This can cause bloating, gas, diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal pain.
Mood swings: An imbalance in gut bacteria may contribute to mood swings, anxiety, and depression.
Autoimmune conditions: There is a growing body of research that suggests a link between gut health and autoimmune conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Unintentional weight changes: When your gut is imbalanced, your body may struggle to absorb nutrients, store fat, and regulate blood sugar. This can lead to unexplained weight gain or loss.
If you notice these signs they indicate your gut health is not optimal, consider incorporating the lifestyle and dietary changes mentioned to prevent further deterioration. Ultimately, consult your doctor if you experience any sign.
YOU MAY LIKE: 8 Foods That Cause Belly Bloating Aside From Bread