Subdivision Of Urinary Tract
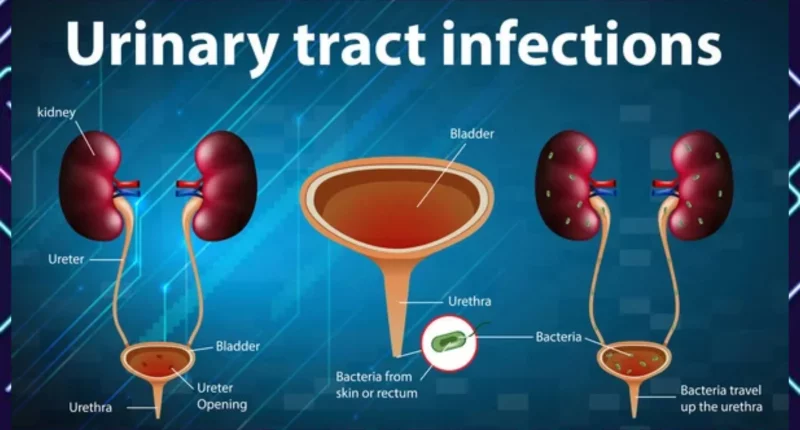
The urinary tract is a complex system responsible for the production, storage, and elimination of urine from the body. This intricate system can be divided into two main components: the upper urinary tract and the lower urinary tract.
The Upper Urinary Tract – The upper urinary tract consists of the kidneys and the ureters. The kidneys are the vital organs that filter waste and excess water from the blood, producing urine. The ureters are the tubes that carry the urine from the kidneys to the bladder. The upper urinary tract can be susceptible to urinary tract infections (UTIs), which can be potentially life-threatening if left untreated. In some cases, the infection can spread from the kidneys into the bloodstream, leading to a serious condition called urosepsis. Urosepsis can cause dangerously low blood pressure, shock, and even death if not promptly addressed.
Symptoms of upper tract UTI include:
- pain and tenderness in the upper back and sides
- chills
- fever
- nausea
- vomiting
The Lower Urinary Tract – The lower urinary tract comprises the bladder and the urethra. The bladder is a hollow, muscular organ that stores the urine produced by the kidneys until it is ready to be eliminated from the body. The urethra is the tube that carries the urine from the bladder to the outside of the body.
Infections and other issues within the lower urinary tract can also lead to various health problems, such as urinary incontinence, overactive bladder, and kidney stones. Maintaining good urinary tract health is essential for overall well-being.
Typical symptoms of lower tract UTI include:
- burning with urination
- increased frequency of urination without passing much urine
- increased urgency of urination
- bloody urine
- cloudy urine
- urine that looks like cola or tea
- urine that has a strong odor
- pelvic pain in women
- rectal pain in men
Sexually active women are more likely to have Urinary tract infections or infections of the bladder or the kidneys. This does not in any way exclude men as theirs mostly occur after the age of 50. Research revealed that by the age of 24, one-third of women are likely to experience at least one episode of urinary tract infection (UTI) that requires antimicrobial treatment. Additionally, 40 to 50% of women will experience at least one UTI episode during their lifetime.
ALSO READ: Want to treat yeast infection? Try these herbal remedies for candida
What You Should Do
1. To be sure of your health status, you can self-check your status using URISTAT UTI Relief Pak at your convenience if you are too busy or don’t feel comfortable visiting a doctor yet.
2. If any of the symptoms above arise in your body, opt for antibacterial protection that can relieve you of pains and sustain you before you visit a doctor. Products like, AZO Urinary Tract Defense Antibacterial Protection are fast and effective to go to.
3. Take antibiotics as prescribed by your physician. Make sure to take all the medication even though the symptoms disappear because if you stop the treatment early, some of the bacteria may survive and infect you again.
4. Have plenty of rest and if the fever persists for long, stay in bed until it gets to normal and you feel better.
5. Drink 6 to 8 soda glasses of fluids especially water each day to flush out your kidneys and wash out the germs from your urinary tract. If you drink cranberry juice or take vitamin C it shall help to make your urine more acid and keep the infection under control.
6. Urinate as often as you feel the urge and try to empty the bladder completely every time before and after sex.
7. Avoid intake of caffeine or alcohol during the treatment as this irritates the bladder.
8. Take showers rather than taking a bath each day and wash the genital area with soap and water. Never use bubble baths or bath oils.
9. Also remember to wipe from front to back after urinating or having a bowel movement because this reduces the chances of germs getting into the bladder. It is also advisable to wear pants with a cotton crotch.
10. Maintain your follow-up visits regularly to cure the infection or else the lingering infection could even damage the kidneys.
While UTIs are usually treated with a course of antibiotics, it’s worth mentioning that severe upper UTIs may require hospitalization.
References
- NHS. Urinary tract infections (UTIs). https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/urinary-tract-infections-utis/
- Nidirect. Urinary tract infections in adults. https://www.nidirect.gov.uk/conditions/urinary-tract-infections-adults
- Medical News Today. Everything you should know about urinary tract infections. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/189953.